Yogurt consumption is linked with healthier diet ” is one is one of the 10 evidence-based conclusions made by the YINI board about the health effects of yogurt… learn more below
Yogurt consumption is a marker of a healthier diet and lifestyle
Numerous studies suggest yogurt consumption is a signature of a healthy diet and lifestyle.
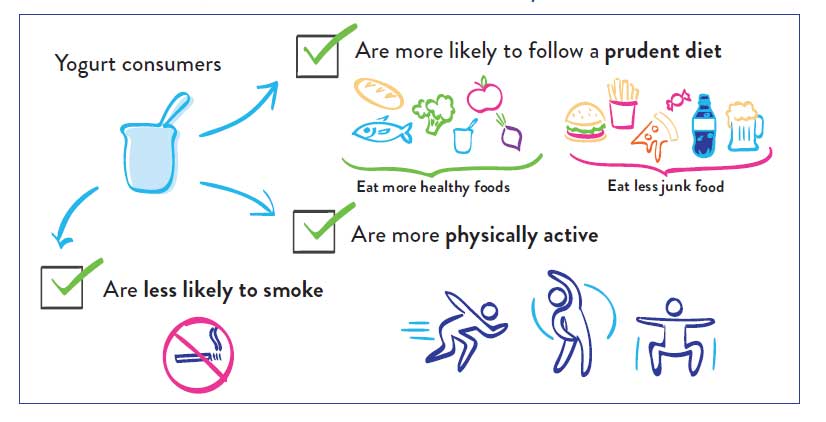
Compared with people who do not eat yogurt, those who do consume yogurt:
- are generally healthier, leaner, more highly educated and of higher socio-economic status
- show healthier non-nutritional behaviour than non-consumers: they are less likely to smoke,19,26,31-33 tend to drink less alcohol and are more likely to be physically active in their leisure time than non-consumers.
- are more aware of the links between food and health, and are more likely to read food labels and less likely to go to fast food restaurants.
- tend to have a better health-related quality of life and mental health.
Yogurt consumption is linked with a lower risk of a variety of chronic diseases.
“Yogurt consumers are characterised by healthier dietary habits than non-consumers and are also known to display healthier non-nutritional behaviours. This has led to the proposal that yogurt consumption may represent the signature of a healthy diet and lifestyle.” – Dr Angelo Tremblay
References:
-
Williams EB, Hooper B, Spiro A, et al. The contribution of yogurt to nutrient intakes across the life course. Nutrition Bulletin 2015;40:9–32.
-
Wang H, Livingston KA, Fox CS, et al. Yogurt consumption is associated with better diet quality and metabolic profile in American men and women. Nutr Res 2013;33:18–26.
-
Zhu Y, Wang H, Hollis JH, et al. The associations between yogurt consumption, diet quality, and metabolic profiles in children in the USA. Eur J Nutr 2015;54:543–50.
-
Panahi S, Fernandez MA, Marette A et al. Yogurt, diet quality and lifestyle factors. Eur J Clin Nutr 2017;71:573–9.
-
Cormier H, Thifault É, Garneau V, et al. Association between yogurt consumption, dietary patterns, and cardio-metabolic risk factors. Eur J Nutr 2016;55:577–87.
-
Hobbs DA, Givens DI, Lovegrove JA. Yogurt consumption is associated with higher nutrient intake, diet quality and favourable metabolic profile in children: a cross-sectional analysis using data from years 1–4 of the National diet and Nutrition Survey, UK. Eur J Nutr 2018.
-
Lecerf J-M, Colin J, Hebel P, et al. Les consommateurs de produits laitiers frais : des consommateurs comme les autres? Analyse de leurs profils alimentaires et nutritionnels (Who are fresh dairy products consumers? Analysis of their dietary and nutritional profiles). Nutrition clinique et métabolisme 2016;30:11–21.
-
Tremblay A, Panahi S. Yogurt consumption as a signature of a healthy diet and lifestyle. J Nutr 2017;147:1476S–80S.
-
Possa G. Corrente JE, Fisberg M. Yogurt consumption is associated with a better lifestyle in Brazilian population. BMC Nutrition 2017;3:29.
-
Possa G, de Castro MA, Marchioni DM, et al. Probability and amounts of yogurt intake are differently affected by sociodemographic, economic, and lifestyle factors in adults and the elderly – results from a population-based study. Nutr Res 2015;35:700–6.
-
D’Addezio L, Mistura L, Sette S, et al. Sociodemographic and lifestyle characteristics of yogurt consumers in Italy: results from the INRAN-SCAI 2005–06 survey. Mediterranean Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism 2015;8: 119–29.
-
Gopinath B, Flood VM, Burlutsky G, et al. Dairy food consumption and health-related quality of life in boys: preliminary findings from a 5-year cohort study. J Am Coll Nutr 2016;35:522–8.
-
Thorning TK, Raben A, Tholstrup T, et al. Milk and dairy products: good or bad for human health? An assessment of the totality of scientific evidence. Food Nutr Res 2016;60:32527.



