Dairy products are a source of lipids, essential for the body’s proper functioning. For example, lipids are source of energy or contribute to nervous system functions. Let’s focus on the types of lipid we can find in dairy products and effects on health.
Brief overview of lipids
There are 3 main types of lipids that can be found in food (2):
- Triglycerides
- Phospholipids
- Steroids
Triglycerides and phospholipids are composed of fatty acids which can be divided into 3 groups: Saturated, Mono-unsaturated, and Poly-unsaturated (link to previous post).
Milk lipids overall content
98% of lipids in milk are triglycerides, the rest comprises of phospholipids, cholesterol and free fatty acids. Milk fatty acids are composed of 3% poly-unsaturated, 25% mono-unsaturated, and 72% saturated fatty acids (1).
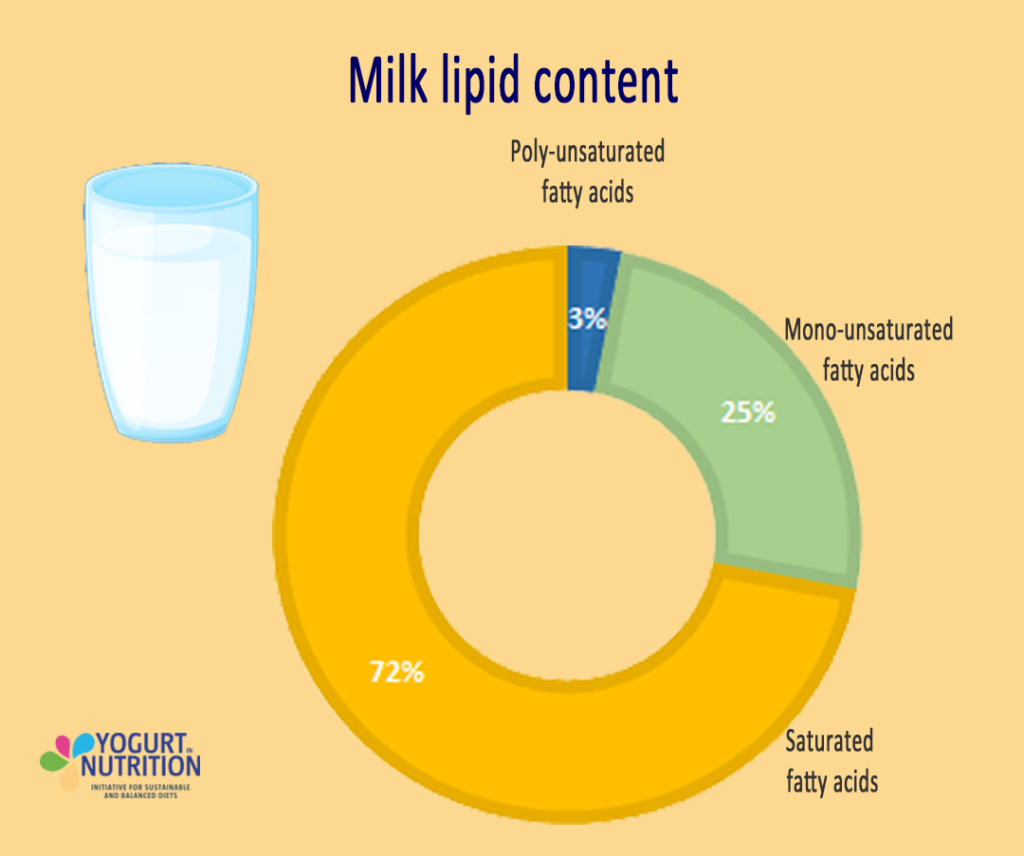
Milk is also a natural source of medium-chain saturated fatty acids (MCFAs), which accounts for 7–8% of total saturated fatty acids in dairy. MCFAs are a rapid source of energy and are thus less likely to be stored in adipose tissue. The rest of the saturated fatty acids are mostly long chain saturated fatty acids.
Lipids in yogurt
The amount of lipids in yogurt depends on which type of milk (whole milk, skimmed milk…) is used and the manufacturing (8).
A plain yogurt contains about 2.3% of total fat (1.5% of saturated fats) when a Greek-style yogurt can contains up to 9% of total lipids (6.2% of saturated fats).

Effects of yogurt lipids on health
Over half of the fat contained in yogurt is saturated fats, with Long Chain saturated Fatty Acids (LCFAs) being the most abundant. LCFAs are usually associated with increased risks of cardiovascular diseases (CVD).
However, in yogurt, studies showed that LCFAs exert a neutral effect on cardiovascular disease risk (3-7). Some even found a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes in those consuming fat from fermented dairy. Researchers noted the risk was reduced only when consuming fermented dairy. The mechanisms as to why this occurs are still relatively unknown, but this could be due to the food matrix of fermented dairy food which differs from regular dairy and the combination of fats with the other nutrients present in yogurt.
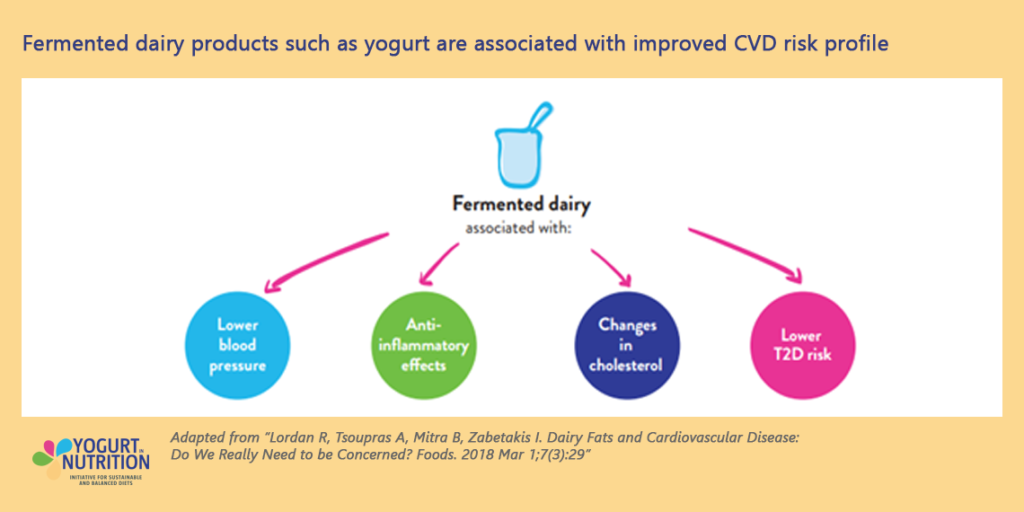
Consuming fermented dairy products have also been associated with lower blood pressure, anti-inflammatory effects, lower cholesterol and lower type 2 diabetes risk which all help reduce cardiovascular disease risk (5).
When producing yogurt, the fermentation of milk by lactic bacteria can release bioactive peptides, which can also act positively against cardiometabolic disease risk (3).
Dairy in the diet
It is recommended to consume 2 to 3 portions of dairy per day. Fats contained in yogurt help with the absorption of fat-soluble nutrients present in yogurt and creates a less acidic taste, which increases its palatability and reduces the need to add sugar. This makes it interesting to choose a yogurt that contains some fat.