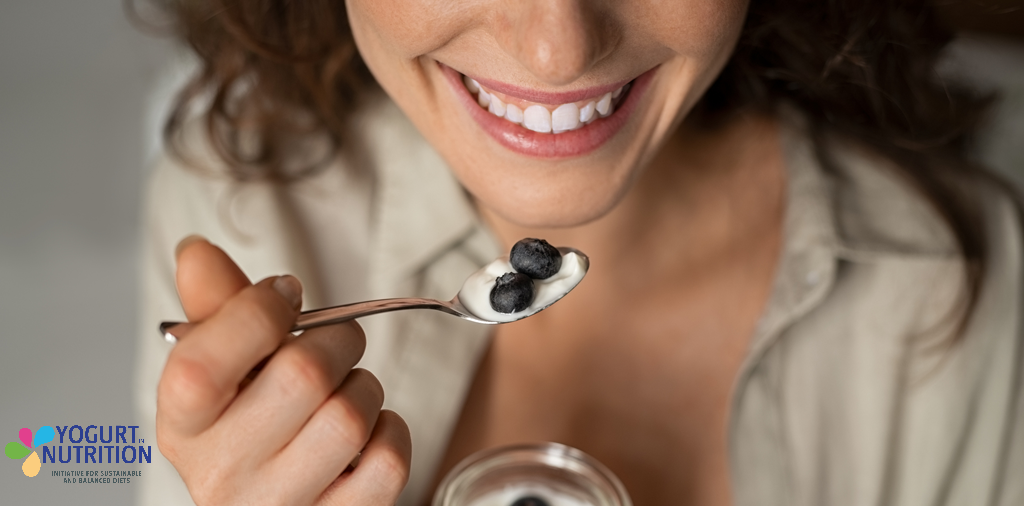
Does the secret to a sparkling healthy smile lie in an everyday serving of yogurt? Latest research suggests that eating yogurt or other probiotic-containing dairy products may help protect us from tooth decay and gum disease, the main causes of tooth loss. A daily dose of dairy could be a ticket to support a healthy set of gnashers – helping to keep the dentist’s drill at bay (1).
The benefits may be achieved thanks to the ability of the probiotics in the dairy product to modify the microbiota living in our mouth, and so to interfere with the decay-causing bacteria that can lead to oral disease, the evidence suggests.
Promising results from trials with probiotics in oral health have led to a flurry of research to find the best probiotic strains, their concentration and how they should be taken.
In an overview of such studies examining the use of probiotics in dentistry around the world, the researchers concluded that probiotic dairy products could reduce dental caries and improve gum health in all ages.
Their analysis of results from 191 studies revealed that, while pharmaceutical formulas were the most used for administering probiotics, several dairy products were also used, including milk, fermented milk, yogurt, kefir, curd, and cheese. Most studies of dairy products as ‘vehicles’ for probiotics have used Lactobacillus strains of microbiota.
Probiotic dairy products may combat tooth decay and plaque
Tooth decay, or dental caries, is damage to a tooth that can happen when ‘bad’ bacteria in your mouth (Streptococcus mutans) produce acids that attack the enamel on the surface of the tooth. It’s encouraged by a sugary diet.
The research has shown that consuming probiotic dairy products could improve the oral microbiota profile and hamper the development of caries in children, adolescents, adults and elderly. The probiotic effect on dental caries is related mainly to a drop in the amount of the bacterial strain Streptococcus mutans, the studies suggest.
The probiotic organisms in the dairy products are thought to achieve this effect in several ways:
- They can colonise the mouth where they compete with mutans for nutrients, effectively starving out the harmful bacteria.
- they may stick to the tooth surface, and may form a barrier, preventing the colonisation by mutans
- they may change the acidity inside the mouth, making it a more hostile environment for mutans
- the reduce acidity may help remineralise tooth mineral structures
The benefits may be particularly good in children, as it seems that their oral microbiota is easily changed compared to adults, the studies suggest.
Yogurt cultures may also have an important role
Products such as yogurts, fermented milks, and some cheeses may have an extra advantage because the starter cultures used to make them, such as S. thermophilus, may help to reduce further the potential for caries (2).
Keep it regular
The studies varied in the type of dairy product they used, the frequency, and duration (ranging from a few weeks to several months). Overall, they showed the importance of regularly consuming the probiotic product to see the health effect. For example, authors of one study recommended drinking probiotic milk every day after they found this was better at inhibiting the caries-causing microorganisms than tri-weekly consumption (3).
However, the probiotic impact may last for 2–4 weeks after you stop consuming it, the research showed.
Periodontal disease may also be hindered by probiotic dairy products
Periodontal diseases are mainly due to chronic inflammation, triggered by harmful bacteria, of the gums and bone that support the teeth. It may start with gingivitis, in which the gums become swollen and may bleed.
The studies showed that probiotic-containing milk, yogurt and cheese are associated with a reduced risk of periodontal disease in children and adults, and improved gum health. (1,3) For example, probiotic yogurt consumption was associated with lower bleeding on probing, and reduced plaque and sore gums.
The studies suggested that, as well as competing with the harmful microorganisms, probiotic dairy may act against periodontal disease through an anti-inflammatory effect in the mouth, reducing swelling of the gums.
Don’t forget, brushing is best
While probiotic dairy products included in a healthy balanced diet may play a valuable role, the best way to keep your teeth and gums in good shape is still to give them a good scrub with the toothbrush, the researchers stress.
‘… the administration of probiotic dairy products could modify the oral microbiota (reductions in S. mutans counts), influence caries development and periodontal disease, or improve gingival health in all subjects (children, adolescents, adults, and the elderly).’ – Farias da Cruz M, et al. 2022
Find out more: read the original article.
Source: (1) Farias da Cruz M, et al. Probiotics and dairy products in dentistry: A bibliometric and critical review of randomized clinical trials. Food Res Int. 2022 Jul;157:111228.
Additionnal references:
-
Sarmento ÉG, et al. Effect of probiotic bacteria in composition of children’s saliva. Food Res Int. 2019 Feb;116:1282-1288.
-
Manmontri C, et al. Reduction of Streptococcus mutans by probiotic milk: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Investig. 2020 Jul;24(7):2363-2374.
-
Yuki O, et al. Effect of bovine milk fermented with Lactobacillus rhamnosus L8020 on periodontal disease in individuals with intellectual disability: a randomized clinical trial. J Appl Oral Sci. 2019 Jul 29;27:e20180564.