Diabetes is a type of disease that has increased in numbers over the past few years.
There are two types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes usually affects young people, and is an autoimmune disease. In this case, the body will “attack” cells responsible for the insulin production. The treatment generally consists of prescribed insulin, diet and physical activities.
- Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) is when the body can’t properly use all the insulin produced or when it can’t control glycemia. It’s more common and generally associated with disbalanced nutritional habits. The fundamental principle of managing T2D is to adopt a healthy lifestyle, which includes a healthy diet, regular physical activity, not smoking and maintaining a healthy weight. [1]
What is the role of diet on Type 2 Diabetes?
Patients with T2 Diabetes will have to manage their diabetes, with medical supports and advices, regular physical activities and a healthy diet.
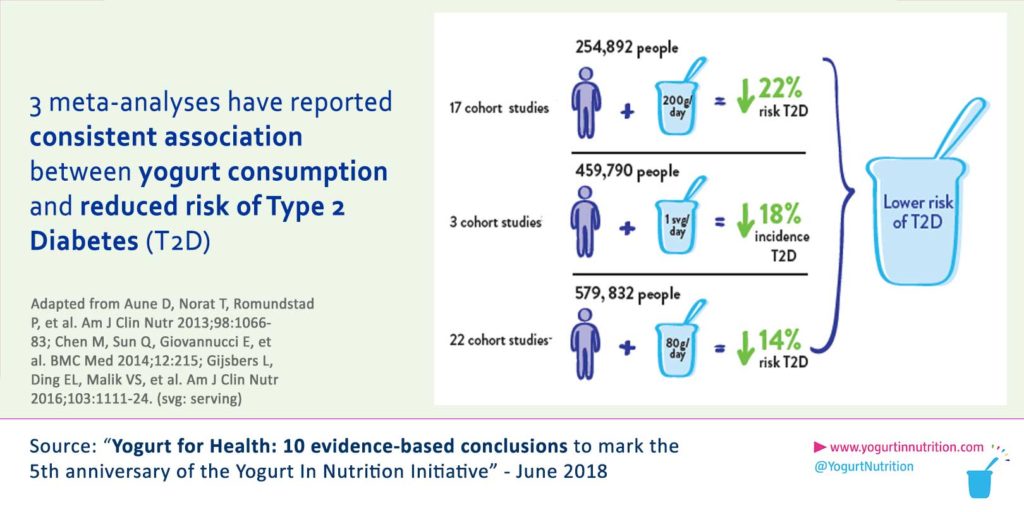
Dairy products, including yogurt, are part of a balanced diet and provide positive effects on health. Moreover, studies have shown an interesting associations between yogurt consumption and reduced risks of type 2 diabetes:
- A study on 4.000 adults over 11 years, showed a strong inverse correlation between T2D and yogurt consumption, compared to non-yogurt consumers (2)
- A meta-analysis, including 194 519 adults, confirmed the specific effect of yogurt on reducing T2D risk (3)
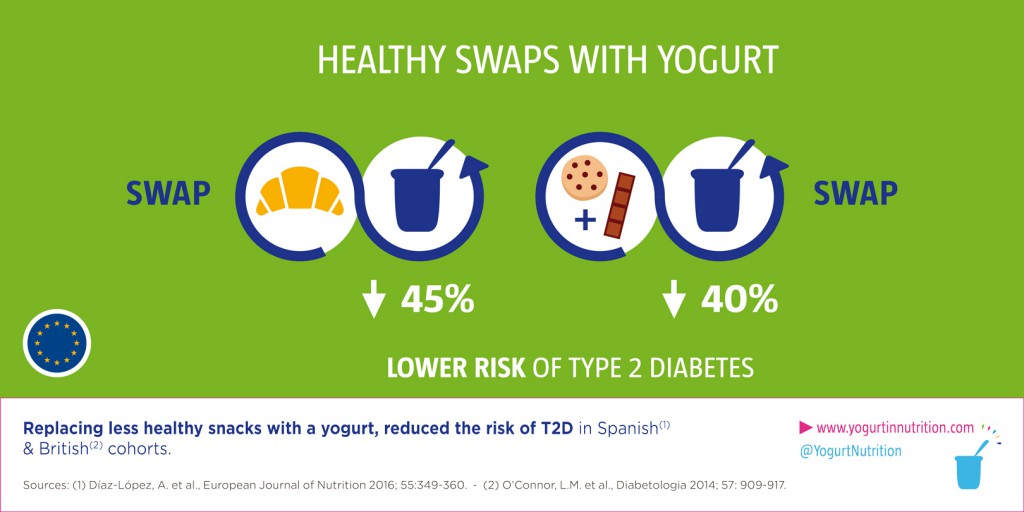
An easy dietary first approach would be to eat yogurts as a snack instead of more “unhealthy” snacks. This substitution has been studied and is correlated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. [2, 4]
How might yogurt help reduce type 2 diabetes risks?
Several biological mechanisms may explain the effects of the yogurt consumption on the reduction of T2 Diabetes risks:
- Yogurt intake is related to lower obesity, which is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes [5]
- The live microorganisms contained in yogurt influence the gut microbiota and may reduce inflammation, which is linked to type 2 diabetes [6, 7]
- Yogurt contains K-2 vitamin, that has been shown to be related to reduced risk for type 2 diabetes [8]
- Yogurt has a low glycemic index and therefore doesn’t cause blood glucose spike [9]
- The proteins in yogurt can stimulate insulin secretion, thus helping with glycemic control [10]
Guidelines for people living with T2D
The main recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO) are to:
- eat a healthy balanced diet
- reduce weight by reducing the food calorie intake
- practice regular daily physical activity appropriate to the physical capabilities
- avoid tobacco and alcohol [1].
Associations around the World recommend consuming three servings of dairy products each day, including yogurt, with no added sugar [11, 12, 13].
You may find more information on yogurt and type 2 diabetes in our Yogurt Nutrition Digest N°8.